 DUALITIES IN JUNGIAN TYPOLOGY
DUALITIES IN JUNGIAN TYPOLOGY
The world is built on universal dualities or pairs of opposites: light - darkness, heat - cold, male - female, creation - destruction, active - passive, up - down, etc. Human nature is such that from any integral phenomenon he can perceive only one pole of it. Only after experiencing the two poles of duality can a person realize the integrity of a certain phenomenon and advance in his development. A person can realize that light and darkness are parts of one whole, that there is no struggle or conflict between them.
Universal dualities in everyday life are experienced by the human psyche as psychological states and attitudes, such as “aggressor-victim”, “euphoria-depression”, “greatness-insignificance”, “good-evil”, “material-spiritual”, etc.
Jungian typology is also built on dualities, it is based on the following pairs of opposites:
Feeling - Thinking,
Sensation - Intuition,
Rationality - Irrationality,
Extraversion - Introversion.
The key element of the Jungian typology is the four psychical functions: Sensation, Feeling, Thinking, and Intuition, and we might also call them four types of intelligence.
Four intelligences – four psychical functions:
• PHYSICAL (or BODY) intelligence – function SENSATION;
• MENTAL intelligence – function THINKING;
• EMOTIONAL intelligence – function FEELING (or EMOTIONS);
• SPIRITUAL intelligence – function INTUITION. The Jungian function of Intuition has much in common with descriptions of Spiritual intelligence.
• People with predominant SENSATION function are well versed in the physical (material) sphere of life, are inclined to interact with physical objects, and are able to work with their hands (making things). They easily identify their own bodily sensations, are tuned to perceive visual-spatial-kinesthetic information (movement, force, external appearance of objects, physical health, physical beauty, color, consistency, taste, temperature, etc.) and are well oriented in space.
• People with the predominant function of FEELING (or emotions) are well oriented in the interpersonal sphere, are versed in relationships, in sympathies and antipathies between people, easily identify their own emotional state and the state of others, are attuned to communication with others. They are inclined to evaluate people and their behavior according to the criteria of "good - bad", "like - dislike" (acceptance or rejection).
• People who have a predominant function of THINKING are well versed in in the sphere of thought, logic, objective facts and patterns, are tuned to intellectual knowledge of objects, analysis, establishment of regularities and cause-effect relationships. They have a clear idea of their goals and know how to prioritize. They are distinguished by precise formulations and attraction to facts and evidence.
• People with predominant function of INTUITION are well versed in the world of ideas, inner meanings of objects, trends, perspectives, unmanifested potentialities, they feel time cycles, the flow of time, the past and the future, the interconnectedness of all things. They have a developed imagination, are perceptive, insightful, inclined to reveal the hidden, are able to perceive the content of the collective and individual unconscious.
In Jung's model of typology, the four psychical functions are represented as dualities: SENSATION is opposite to INTUITION, and FEELING is opposite to THINKING.
These dualities are not just opposites, they are complementary and interdependent. Just as without light there is no shadow, so without Intuition there is no Sensation, and without Thinking there is no Feeling. Changes in one function cause changes in the opposite function and vice versa.
Besides, these two pairs of functions are characterized by different parameters. The pair Sensation - Intuition are irrational functions, while the pair Feeling - Thinking are rational.
It is worth noting that the Jungian term "rationality" is identical to planning, and the term "irrationality" is identical to spontaneous. More on this here >>>
Another basic parameter in Jung’s typology is the duality EXTRAVERSION - INTROVERSION.
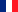
Carl Jung found that any of the four basic psychic functions can have introverted or extraverted orientation depending on the direction of a person's attention: to external objects or inward. Accordingly, each of the four functions has two variants: extraverted and introverted, and together there are eight psychic functions: 4 introverted and 4 extraverted.

• Sensation Extraverted - Se
• Sensation Introverted – Si
• Feeling Extraverted - Fe
• Feeling Introverted – Fi
• Thinking Extraverted - Te
• Thinking Introverted - Ti
• Intuition Extraverted – Ne
• Intuition Introverted – Ni
Extraversion - Introversion are widely used terms, but far from what Carl Jung meant by them. Jungian Extraversion - Introversion is not the same as gregarious - reserved. An introvert can be more sociable than an extrovert. In addition, there are 4 types of introverts and 4 types of extroverts, each with their own characteristics.
All eight functions are present in the psyche of each person, but they have different degrees of development. One of the functions always surpasses the others in strength, speed of reaction and meaningfulness of this reaction. It is called the main one.
Carl Jung wrote: “Just as a lion strikes down his enemy or his prey with his fore-paw, in which his strength resides, and not with his tail like the crocodile, so our habitual reactions are normally characterized by the application of our most trustworthy and efficient function; it is an expression of our strength. However, this does not prevent our reacting occasionally in a way that reveals our specific weakness. The predominance of a function leads us to construct or to seek out certain situations while we avoid others, and therefore to have experiences that are peculiar to us and different from those of other people. An intelligent man will make his adaptation to the world through his intelligence, and not in the manner of a sixth-rate pugilist, even though now and then, in a fit of rage, he may make use of his fists. In the struggle for existence and adaptation everyone instinctively uses his most developed function, which thus becomes the criterion of his habitual reactions.” (1)
The type of person is determined by the main psychic function. If the main (dominant) function is Sensation Extraverted, then the type is called Sensing Extraverted (Se), if the main function is Feeling Introverted, then the type is called Feeling Introverted (Fi), etc.
The basic elements of Jung's typology are eight psychological types. They are innate and do not change during life.
Each psychotype can have both strengths and weaknesses.
* The strong side of the Se type is courage, determination, the ability to physically confront opponents and take the lead of others in critical situations. The weak side is the impulsiveness of actions without thinking the consequences through.
* The strong side of Si type is the ability to create physical comfort and coziness, care for good health, reconciliation of conflicting parties. The weak side is inertia, avoidance of discomfort and psychological tension.
* The strong side of Fe type is feeling the emotional state of others, ability to establish emotional connection with others, to provide emotional support, to inspire. The weak side is hyperbolization of feelings and their contradiction.
* The strong side of Fi type is empathy, ordering a huge amount of connections, establishing rules of communication and moral standards. The weak side is conservatism and condemnation of those who do not share his or her values.
* The strong side of Te type is the ability to manage resources and find effective ways to achieve practical results, introduction of new technologies. The weakness is that the achievement of goals is more important than relations with people, as well as the focus on quick results.
* The strong side of Ti type is the ability to analyze, get to the bottom of problems, establish cause and effect relationships, find patterns and create systems. The weakness is the rejection of facts that may violate one’s theory/concept, as well as emotional coldness and detachment.
* The strong side of Ne type is inventiveness, the ability to find a way out of different situations, the capacity to see potential opportunities and the interconnectedness of all things. The weak side is excessive fantasizing, changeability and impracticality.
* The strong side of Ni type is the feeling of the hidden, unconscious, the inner state of others, the flow of time, premonition and foresight of the development of events. The weak side is unwillingness to act, uncertainty, over-sensitivity.
Once we have learned to discern the qualities of a type and know which qualities in us are stronger and which are weaker, then we can try to develop stronger ones and work on what's hindering us.
* * * * *
1 - A lecture delivered at the Congress of Swiss Psychiatrists, Zurich, 1928, and published as “Psychologische Typologie” in Seelenprobleme der Gegenwart (Zurich, 1931)
Last updating 20.04.2024
Original text in Ukrainian here >>>